Run a JSON Model¶
Now let's first try something easy to get you familiar with Pinferecia.
TL;DR
It's important for you to understand how to register and serve a model in Pinferencia.
However, if you want to try machine learning model now, you can jump to Serve Pytorch MNIST Model
Define the JSON Model¶
Let's create a file named app.py.
Below is a JSON Model.
It simply return 1 for input a, 2 for input b, and 0 for other inputs.
| app.py | |
|---|---|
1 2 3 4 | |
Create the Service and Register the Model¶
First we import Server from pinferencia, then create an instance and register a instance of our JSON Model.
| app.py | |
|---|---|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
What are the model_name and entrypoint here?
model_name is the name you give to the model for later API access. Here we give the model a name json, and the url for this model is http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/models/json.
If you have any confusion about the APIs, you can always visit the documentation page mentioned in the next part.
The entrypoint predict means we will use the predict function of JSON Model to predict the data.
Start the Server¶
$ uvicorn app:service --reload
INFO: Started server process [xxxxx]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Open your browser and visit http://127.0.0.1:8000, and now you have an automatically generated API Documentation page!
FastAPI and Starlette
Pinferencia builds on FastAPI which is built on Starlette.
Thanks to them, you will have an API with OpenAPI Specification. It means you will have an automatic documentation webpage and client codes can also be generated automatically.
Tips
There are two API documentation endpoints:
You can view the API specifiacations and even try out the API by yourself!
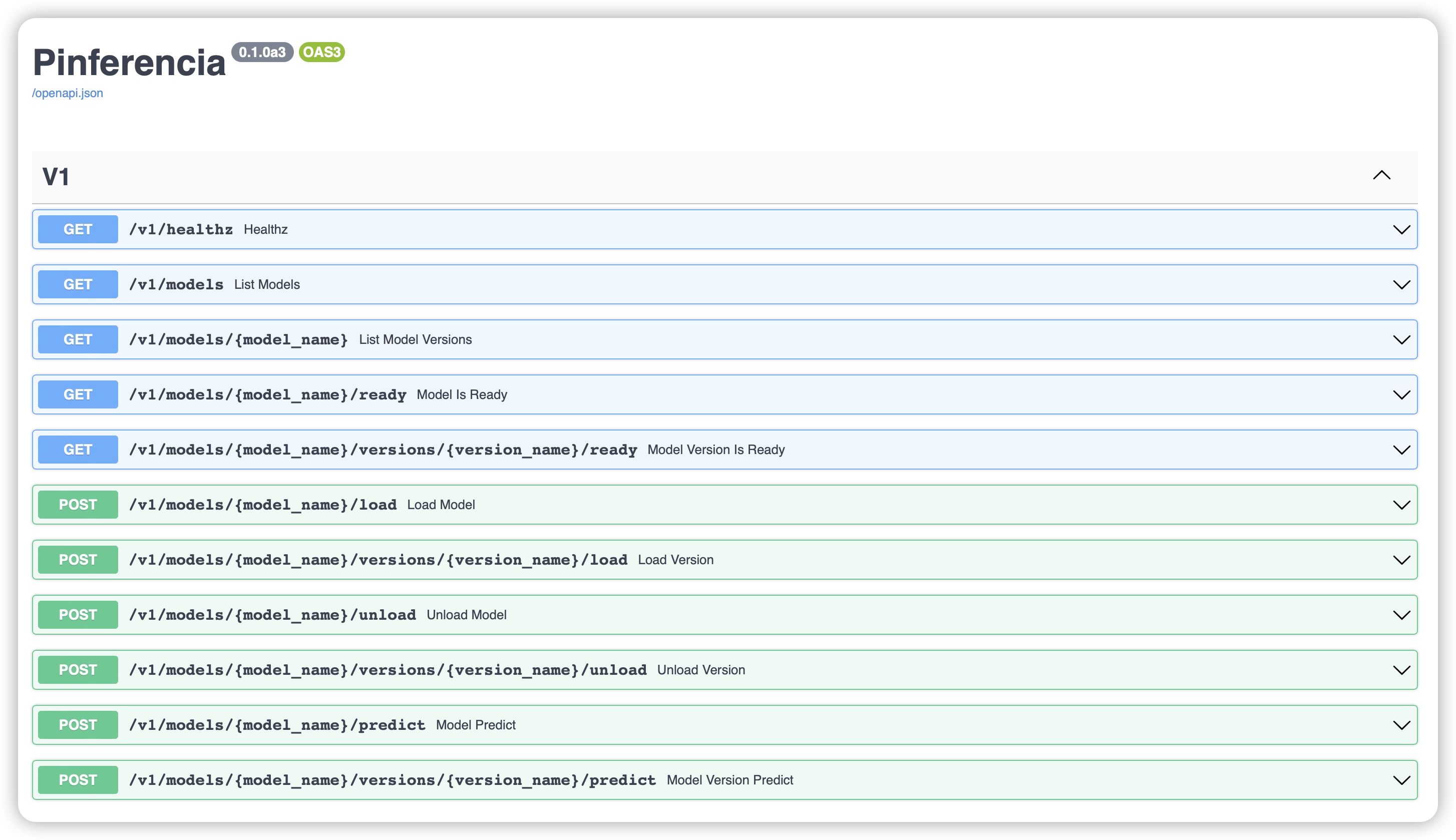
Test the API¶
Create a test.py with the codes below.
Tips
You need to have requests installed.
pip install requests
| test.py | |
|---|---|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
Run the script and check the result.
$ python test.py
{'model_name': 'json', 'data': 1}
Now let's add two more inputs and make the print pretty.
| test.py | |
|---|---|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
Run the script again and check the result.
$ python test.py
| Input | Prediction |
|----------|---------------|
| a | 1 |
| b | 2 |
| c | 0 |